Medical Self-Service Terminal: Innovative Practice in Smart Healthcare Services
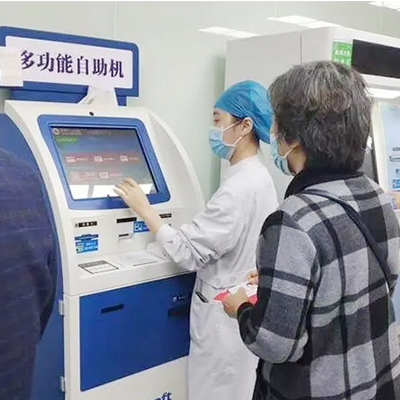

Medical Self-Service Terminal: Innovative Practice in Smart Healthcare Services
I. Core Value of Medical Self-Service Terminals
Medical self-service terminals are a vital component of modern smart healthcare systems. Through technological innovation, they optimize medical service processes, creating multiple benefits for both patients and medical institutions:
Process Redesign
- Restructures traditional patient flow by moving registration, payment, and other processes to self-service terminals
- Enables “in-clinic settlement,” reducing patients’ back-and-forth movement
- Supports time-slot appointments to effectively distribute peak-hour patient flow
Experience Enhancement
- Provides 24/7 uninterrupted service
- Supports multiple payment methods (health insurance cards, e-health insurance, mobile payments)
- Equipped with intelligent guidance systems to optimize patient pathways
II. Key Functional Modules
Outpatient Services
- Smart Registration: Supports department selection, doctor inquiries, and appointment scheduling
- Self-Service Payment: Handles outpatient billing and prescription printing
- Report Inquiry: Allows self-service printing of test and examination results
Inpatient Services
- Hospitalization registration
- Prepaid deposit top-up
- Daily expense inquiries
- Discharge settlement
Convenience Services
- Medical record copy requests
- Invoice printing
- Satisfaction surveys
- Hospital navigation
III. Technological Innovations
Identity Verification Technology
- Supports second-generation ID cards, health insurance cards, and e-health insurance credentials
- Facial recognition with liveness detection
- Fingerprint verification as an auxiliary method
Intelligent Interactive System
- Voice-guided assistance
- Smart form-filling support
- Multilingual service capabilities
Security Assurance System
- Financial-grade encrypted keyboards
- Data desensitization processing
- Operation log tracking
IV. Application Effectiveness Analysis
Patient Benefits
- Average waiting time reduced by 60%
- Non-treatment time decreased from 45% to 15%
- Satisfaction rate increased to over 95%
Hospital Benefits
- Service window pressure reduced by 40%
- Labor costs saved by 30%
- Billing error rate lowered to below 0.1%
Management Improvements
- Real-time data monitoring
- Service process optimization
- Scientific resource allocation
V. Future Development Trends
Functional Expansion
- Integration with internet hospital services
- Addition of health management features
- Support for direct commercial insurance payments
Technological Upgrades
- 5G remote assistance
- AI-based pre-consultation
- Blockchain electronic medical records
Service Extension
- Community healthcare coordination
- Medical consortium resource sharing
- Home health monitoring
VI. Implementation Recommendations
Phased Rollout
- Prioritize outpatient over inpatient services
- Start with tertiary hospitals before expanding to primary care
- Begin with pilot programs before full-scale implementation
Supporting Measures
- Improve operation and maintenance systems
- Strengthen staff training
- Establish contingency mechanisms
Continuous Optimization
- Regular feature updates
- User experience tracking
- Data analysis applications
Conclusion: Medical self-service terminals are reshaping healthcare service models. Their value lies not only in improved efficiency but also in advancing the “patient-centered” service philosophy. With ongoing technological innovation and expanding application scenarios, self-service terminals will become a cornerstone of smart hospital development, injecting new momentum into the enhancement of healthcare service quality.